智能调度,高效赋能:揭秘算力网络资源优化分配之道#
算力网络,简单来说,就是将计算能力像水电一样进行输送的网络。想象一下,我们平时使用的手机、电脑等设备,都需要处理器来计算和运行各种程序。而算力网络就像是一个超级大的"处理器仓库",它将分散在各地的计算资源整合起来,通过互联网进行优化分配,以满足不同用户和场景的计算需求。
举个例子,当我们观看高清视频、玩大型游戏或者进行复杂的数据分析时,这些操作都需要大量的计算能力。算力网络就像是一个智能的"电力系统",能在短时间内为我们提供所需的计算资源,确保我们的使用体验流畅、高效。这样一来,我们就可以随时随地享受到强大的计算能力,而不用担心设备性能不足的问题。
算力网络面临的挑战#
资源分配效率: 算力网络需要高效地分配计算资源以满足不同用户和应用的多样化需求。这要求网络能够实时监测资源使用情况,并动态调整资源分配策略,以避免资源闲置或过载。
网络延迟: 计算任务的快速响应需要低延迟的网络环境。算力网络必须解决数据在网络中传输的延迟问题,特别是在处理实时性要求高的应用时,如自动驾驶等。
成本要低: 搭建和维护算力网络需要投入大量资金,所以需要在保证性能的同时,尽量降低成本。
算力网络的组成部分#
算力网络主要由三个部分组成:
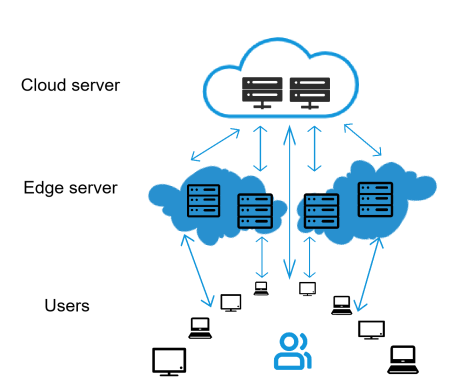
端侧设备: 也就是各种智能设备,它们负责收集数据。
边缘服务器: 位于设备附近,负责处理部分数据,并减轻云端服务器的负担。
云端服务器: 位于数据中心,拥有强大的计算能力,负责处理更复杂的数据。
赛题内容#
考虑一个特定区域的算力网络布局优化问题。将区域划分成若干相邻正方形网格,算力需求分布数据提供了各个网格内的算力需求。数据中的坐标值为所在网格的中心坐标,为简化问题,将各网格内的算力需求点统一到所在网格中心点(即可认为是一个网格对应一个需求点)。
网格内的算力需求由端侧设备产生,端侧设备是连接到网络的终端设备,例如传感器、智能手机、工业机器人等。算力网络中的算力需求由边缘服务器和云端服务器满足。边缘服务器位于网络的"边缘",通常靠近终端用户或设备。它们的任务是在离用户更近的地方处理数据,以提高响应速度和效率。边缘服务器可以更快地处理请求,因为它们距离用户更近。边缘服务器可以减轻核心云基础设施的负担,提高整体操作效率。云端服务器位于远离用户的数据中心,具有强大的计算和存储能力。当边缘服务器容量不足时,云端服务器可以作为补充。边缘服务器和云端服务器之间的协同作用可以优化整个系统的性能和可靠性。
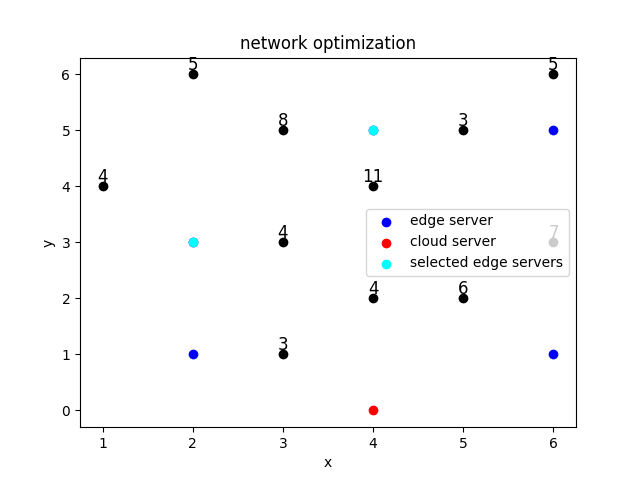
问题1: 在问题1中我们只考虑由边缘服务器满足计算区域内的需求。 假设要在算力需求分布的网格区域内开设2个边缘服务器,每个边缘服务器的覆盖半径为1。 要求建立QUBO模型,确定在哪些点放置边缘服务器可以覆盖最多的算力需求。
问题2: 当边缘服务器无法满足算力需求时,将由上游云端服务器提供计算服务。现在网格区域外部增设云端服务器,端侧和边缘服务器可以选择连接到云端节点,当边缘服务器接受的计算需求超过容量限制时,边缘服务器多余的需求将直接被分配到云端服务器。 每个端侧节点的算力需求都必须被满足,且只能由一个服务器服务,这个计算节点可以是云端节点,也可以是边缘服务器。由于边缘服务器存在资源容量上限约束,假设每个边缘服务器的可用计算资源容量为12,云端服务器的可用计算资源容量为无穷大, 即不考虑云端服务器的可用计算资源限制。服务器存在一定的覆盖半径,假设边缘服务器的覆盖半径为3,云端服务器的覆盖半径为无穷大,即不考虑云端服务器的覆盖范围。
开设边缘服务器通常需要成本,该成本由固定成本,计算成本和传输成本组成。其中固定成本与是否开设以及开设位置有关;计算成本与请求的计算资源量成正比,计算方法为:单位计算成本乘以计算量。云端服务器的单位计算量成本为1,边缘服务器的单位计算量成本为2。 同时,从端侧到边侧、从边侧到云侧、从端侧到云侧之间的传输也存在传输成本,传输成本计算方式为:传输的算力需求量乘以传输距离乘以单位传输成本,其中传输距离的计算使用欧式距离保留两位小数,按照单边距离计算(不考虑往返传输)。从端侧到边侧以及从边侧到云侧的单位传输成本为1,从端侧到云侧的单位传输成本为2。
如果要满足区域内全部的端侧算力需求,建立QUBO模型,求解给出整体成本最小的算力网络布局,即边缘服务器的位置、数量,以及端侧到边侧、边侧到云侧和端侧到云侧节点之间的连接关系。
问题本质#
在算力网络布局优化问题中,表面上看,我们可能会联想到经典的资源调度问题或网络流优化问题,并尝试通过传统的贪心算法或动态规划方法来求解"如何在不同区域间分配资源以最小化成本"。这些方法或许能够帮助我们找到某一时刻的局部最优解,但这个问题的复杂性远超表面。我们不仅需要考虑每个计算节点的资源分配,还要全局性地优化整个网络的布局,保证每个资源都得到合理利用,并且在多个区域之间保持高效的计算和通信。
深入分析#
算力网络布局优化问题的核心是如何在整个网络中找到一种资源分配和节点布局的最优方案,类似于在图G上寻找最优的计算节点布局和通信路径组合。这实际上是一个组合优化问题,需要从所有可能的网络布局中挑选出最优解,而这些可能的布局数目是巨大的。例如,如果我们有n个潜在的边缘服务器部署位置和m个计算任务点,那么这些位置和任务的组合数量将以指数级别增长,即n^m种可能的布局方式。
显然,简单的穷举法是不现实的,因为即使是中等规模的网络,其组合数量也是天文数字,远远超出了经典计算机的处理能力。就像旅行商问题中的路径选择一样,我们在这里面临着一个排列组合的难题,网络中的每个节点和资源配置都可能影响整体的优化结果。
换句话说,随着问题规模的扩大,算法的时间复杂度呈现非多项式增长,难以在合理时间内求解。由此可见,问题的关键并不在于如何局部优化某一个资源配置,而在于如何全局性地优化整个算力网络的布局,找到那条能够最小化整体计算成本的最优布局路径。这个问题的复杂性不仅仅是计算量的增加,更在于需要在多维度上同时进行优化,寻找全局最优解。
第一问参考模型#
第一问重述#
在一个4x4的网格中,每个网格代表一定的计算需求区域。我们的目标是确定在哪些网格中部署边缘计算节点,以便最大化覆盖的用户需求。
符号定义#
: 边缘计算节点的覆盖半径。
: 计划部署的边缘计算节点个数。
: 用户位置集合。
: 候选边缘节点位置集合。
: 位于网格
处的算力需求量。
: 网格
和
之间的距离。
: 网格
和网格
之间的距离是否不超过边缘节点覆盖半径
。
决策变量#
: 一个二进制变量,表示是否在网格
部署边缘计算节点。
: 一个二进制变量,表示网格
是否被覆盖。
目标函数#
最大化总覆盖的计算需求量:
约束条件#
每个用户网格的覆盖状态不超过其周围边缘节点的覆盖状态:
部署的边缘计算节点总数等于
:
简化模型(容斥原理)#
当 时,我们可以使用容斥原理来简化模型:
第二问参考模型#
问题概述#
6×6的网格,每个网格内都有一定的计算需求(只有11个网格中的计算需求为非零值),需要满足所有计算需求
5个开设边缘服务器的候选位置,边缘服务器具有计算容量限制; 当边缘服务器接收的计算请求超过容量时,将多出的计算请求发送给云端服务器
1个位置开设了云端服务器,云端服务器无容量限制
用户可以连接边缘服务器或者云端服务器(只能连一个); 边缘服务器容量不够可以连接云端服务器
最小化成本:固定成本 + 可变成本(计算成本) + 传输成本(=单位成本*距离*传输量)
符号定义#
: 边侧服务器容量。
: 边缘计算节点开设在网格
的固定成本。
: 云侧节点的单位计算量成本。
: 边侧节点的单位计算量成本。
: 从端侧到边侧的单位传输成本。
: 从端侧到云侧的单位传输成本。
: 从边侧到云侧的单位传输成本。
: 网格
和
之间的距离。
: 网格
和云端服务器之间的距离。
: 网格
和网格
之间的距离是否不超过边缘节点覆盖半径
。
中间变量#
: 网格
的需求是否由位于网格
的边侧服务器服务。
: 网格
的边侧服务器是否连接云端服务器。
: 网格
的需求是否由云端服务器服务。
: 超过边侧服务器
的容量的计算需求中,由云端服务器服务的数量。
决策变量#
: 是否在位置
处开设边侧服务器。
数学模型#
目标函数:
其中
本模型中,我们将 表示为
同时我们添加约束条件,使得当且仅当边侧服务器 收到的计算需求超过其容量限制时,
才会取值为
,否则取值为
。虽然
的表达式中出现了二次项,但是本模型中云端服务器没有容量限制,
只出现在目标函数中,而不会出现在约束中,从而保证了转化成QUBO模型时不会出现高阶项。
约束条件:
算力需求点被分配到边侧或云侧,且只被一个服务
覆盖关系,且只有开了边侧才可以从需求点连接
边侧连接云侧和开启边侧的关系
当且仅当边侧服务器
收到的计算需求超过其容量限制时,
取值为
其中
为边侧服务器
接收的计算需求的上界,这里我们令
预处理#
对于边侧服务器候选位置 ,如果其接收的计算需求始终小于边侧服务器容量限制,例如
成立时,可以令 ,并且对于该候选位置,可以不考虑不等式约束 (1) 和 (2),减少比特数(松弛变量数量)。
第一问代码#
1"""
2JSP Problem Solving
3"""
4import math
5import numpy as np
6import kaiwu as kw
7
8
9class JSPSolver:
10 """Solver for JSP optimization problem."""
11
12 def __init__(
13 self,
14 num_nodes: int = 2,
15 coverage_range: float = 2.0,
16 penalty: float = 100.0,
17 num_slack_bins: int = 1,
18 ) -> None:
19 """Initialize JSPSolver parameters.
20
21 Args:
22 num_nodes: Number of edge nodes to be selected.
23
24 coverage_range: Node coverage threshold.
25
26 penalty: penalty coefficient.
27
28 num_slack_bins: Slack binary digits, used to override constraints.
29 """
30 self.num_nodes = num_nodes
31 self.coverage_range = coverage_range
32 self.penalty = penalty
33 self.num_slack_bins = num_slack_bins
34
35 # Data containers
36 self.demand = {}
37 self.locations = []
38 self.distances = {}
39 self.coverage = {}
40 self.dimension = 0
41
42 # QUBO model
43 self.model = None
44
45 def prepare_data(self, demand_data):
46 """prepare demand, distance, and coverage matrix data.
47
48 Args:
49 demand_data: dict, the key is the coordinate string 'i, j',
50 and the value corresponds to the calculation requirement.
51 """
52 self.demand = demand_data
53 # Create a list containing all location coordinates
54 self.locations = list(demand_data.keys())
55 # Calculate the number of location coordinates
56 self.dimension = int(math.sqrt(len(self.demand)))
57 # Iterate through all location coordinates to calculate distances between pairs
58 self.distances = {
59 (i, j): np.linalg.norm(
60 np.array([int(coord) for coord in i.split(',')])
61 - np.array([int(coord) for coord in j.split(',')])
62 )
63 for i in self.locations
64 for j in self.locations
65 }
66 # Initialize a dictionary to store the coverage relationship between locations
67 self.coverage = {
68 (i, j): int(dist <= self.coverage_range)
69 for (i, j), dist in self.distances.items()
70 }
71
72 def prepare_model(self):
73 """Building a Qubo Model
74 """
75 # Create binary variable arrays x and z to represent edge computing node locations
76 # and demand coverage conditions
77 var_x = kw.core.ndarray((self.dimension, self.dimension), 'x', kw.core.Binary)
78 var_z = kw.core.ndarray((self.dimension, self.dimension), 'z', kw.core.Binary)
79 # Initialize slack variables
80 slack = kw.core.ndarray((self.dimension, self.dimension, self.num_slack_bins), 'slack',
81 kw.core.Binary)
82 # Define the objective function to minimize the total computing power demand
83 obj = sum(
84 self.demand[f'{i + 1},{j + 1}'] * var_z[i, j]
85 for i in range(self.dimension)
86 for j in range(self.dimension)
87 )
88 # Define the first constraint, ensuring the number of edge computing nodes equals P
89 constr1 = (np.sum(var_x) - self.num_nodes) ** 2
90 # Initialize the second constraint
91 constr2 = 0
92 # Iterate through all location coordinates to build the second constraint
93 for i in range(self.dimension):
94 for j in range(self.dimension):
95 # For each location, the demand coverage z[i] should be less than or equal to
96 # the total coverage provided by all edge computing nodes
97 constr2 += (var_z[i, j] + sum(slack[i, j, _] * (2 ** i) for _ in range(self.num_slack_bins))
98 - sum(self.coverage[f'{i + 1},{j + 1}', f'{i1 + 1},{j1 + 1}'] * var_x[i1, j1]
99 for i1 in range(self.dimension) for j1 in range(self.dimension))) ** 2
100
101 self.model = kw.qubo.QuboModel()
102 self.model.set_objective(-obj)
103 self.model.add_constraint(constr1 == 0, name='c1', penalty=self.penalty)
104 self.model.add_constraint(constr2 == 0, name='c2', penalty=self.penalty)
105
106 def solve(self):
107 """Solving the QUBO model.
108
109 Returns:
110 tuple: Result dictionary and Result dictionary.
111
112 - dict: Result dictionary. The key is the variable name, and the value is the corresponding spin value.
113
114 - float: qubo value.
115 """
116 # Perform the Simulated Annealing algorithm
117 worker = kw.classical.SimulatedAnnealingOptimizer(
118 initial_temperature=100000,
119 alpha=0.99,
120 cutoff_temperature=0.0001,
121 iterations_per_t=100,
122 rand_seed=10)
123 _solver = kw.solver.SimpleSolver(worker)
124 _sol_dict, _qubo_value = _solver.solve_qubo(self.model)
125 return _sol_dict, float(_qubo_value)
126
127 def recovery(self, sol_dict):
128 """Verify whether the solution is feasible"""
129 return self.model.verify_constraint(sol_dict)
130
131
132if __name__ == "__main__":
133 # Store computing power demand data in the DEM dictionary,
134 # where the keys are location coordinates and the values are computing power demands
135 demand_data = {'1,1': 38, '1,2': 22, '1,3': 65, '1,4': 56,
136 '2,1': 53, '2,2': 48, '2,3': 76, '2,4': 46,
137 '3,1': 56, '3,2': 36, '3,3': 7, '3,4': 29,
138 '4,1': 50, '4,2': 37, '4,3': 48, '4,4': 40}
139 # Create an instance of the CIMSolver class
140 solver = JSPSolver()
141
142 # Prepare data
143 solver.prepare_data(demand_data)
144
145 # Prepare the QUBO model with a specified penalty coefficient lambda
146 solver.prepare_model()
147
148 # Use the Simulated Annealing algorithm to find the optimal solution
149 best_sol_dict, qubo_value = solver.solve()
150
151 # Recover the original problem solution from the QUBO solution and check its feasibility
152 unsatisfied_count, result_dict = solver.recovery(best_sol_dict)
153 if unsatisfied_count == 0:
154 print("Find a feasible solution")
155 print('Objective value:', -qubo_value)
156 else:
157 print("No feasible solution")
第二问代码#
1"""Cloud-Edge-User Cost Minimization QUBO Model Solver."""
2import math
3from typing import Tuple
4import numpy as np
5import kaiwu as kw
6
7
8class CloudEdgeUserSolver:
9 """Solver for cloud-edge-user cost-minimization QUBO model."""
10
11 def __init__(
12 self,
13 edge_capacity: int = 12,
14 edge_radius: float = 3.0
15 ) -> None:
16 """Initialize core parameters and placeholders."""
17 # capacities and radii
18 self.edge_capacity = edge_capacity
19 self.edge_radius = edge_radius
20
21 # Service node configurations
22 self.user_locations = ['1,1', '1,4', '2,6', '3,3', '3,5', '4,4', '5,5', '6,3', '6,6']
23 self.edge_locations = ['6,1', '2,3', '4,5', '6,5']
24 self.cloud_locations = ['4,0']
25
26 # edge server costs
27 self.fix_cost_edge = {'6,1': 60, '2,3': 42, '4,5': 46, '6,5': 54}
28
29 # variable costs
30 self.var_cost_cloud = 1
31 self.var_cost_edge = 2
32
33 # Unit transmission cost
34 self.trans_cost_user_edge = 1
35 self.trans_cost_user_cloud = 2
36 self.trans_cost_edge_cloud = 1
37
38 # Demand data
39 self.demand = {
40 '1,1': 7, '1,4': 4, '2,6': 5,
41 '3,3': 9, '3,5': 8, '4,4': 11,
42 '5,5': 1, '6,3': 7, '6,6': 5
43 }
44
45 # Precomputed data
46 self.num_user = 0
47 self.num_edge = 0
48 self.num_cloud = 0
49 self.distances = {}
50 self.coverage = {}
51 self.qubo_model = None
52
53 def prepare_data(self):
54 """Prepare data for QUBO model."""
55 # initialize user demands
56 loc_set_inner_full = ['1,1', '1,2', '1,3', '1,4', '1,5', '1,6',
57 '2,1', '2,2', '2,3', '2,4', '2,5', '2,6',
58 '3,1', '3,2', '3,3', '3,4', '3,5',
59 '4,1', '4,2', '4,3', '4,4', '4,5', '4,6',
60 '5,1', '5,2', '5,3', '5,4', '5,5', '5,6',
61 '6,1', '6,2', '6,3', '6,4', '6,5', '6,6']
62 # all nodes
63 loc_set = loc_set_inner_full + self.cloud_locations
64
65 self.num_cloud = len(self.cloud_locations)
66 self.num_edge = len(self.edge_locations)
67 self.num_user = len(self.user_locations)
68
69 # compute distances
70 for i in loc_set:
71 for j in loc_set:
72 self.distances[(i, j)] = round(np.sqrt(
73 (int(i.split(',', maxsplit=1)[0]) - int(j.split(',', maxsplit=1)[0])) ** 2 + (
74 int(i.split(',', maxsplit=1)[1]) - int(j.split(',', maxsplit=1)[1])) ** 2), 2)
75
76 # compute coverage relationships
77 for i in loc_set:
78 for j in loc_set:
79 if self.distances[(i, j)] <= self.edge_radius:
80 self.coverage[(i, j)] = 1
81 else:
82 self.coverage[(i, j)] = 0
83
84 def prepare_model(
85 self,
86 eq_penalties: Tuple[float, float, float] = (1e4, 1e4, 1e4),
87 ineq_penalties: Tuple[float, float] = (1e4, 1e4)
88 ) -> None:
89 """
90 Build QUBO with 3 equality and 2 inequality constraints.
91 """
92 # compute the maximum demand for each edge
93 max_ujk = []
94 for j in self.edge_locations:
95 max_ujk.append(sum(self.demand[i] * self.coverage[i, j] for i in self.user_locations))
96
97 # initialize decision variables
98 x_edge = kw.core.ndarray(self.num_edge, 'x_edge', kw.core.Binary)
99 y_ij = kw.core.ndarray((self.num_user, self.num_edge), 'yij', kw.core.Binary)
100 y_jk = kw.core.ndarray((self.num_edge, self.num_cloud), 'yjk', kw.core.Binary)
101 y_ik = kw.core.ndarray((self.num_user, self.num_cloud), 'yik', kw.core.Binary)
102
103 # for each edge, if the maximum demand does not exceed the edge's capacity, set the corresponding yjk to 0
104 for j in range(self.num_edge):
105 if max_ujk[j] <= self.edge_capacity:
106 y_jk[j][0] = 0
107
108 # initialize ujk related variables
109 u_jk = np.zeros(shape=(self.num_edge, self.num_cloud), dtype=kw.core.BinaryExpression)
110 ujk_residual = np.zeros(shape=self.num_edge, dtype=kw.core.BinaryExpression)
111 for j in range(self.num_edge):
112 ujk_residual[j] = sum(
113 self.demand[self.user_locations[i]] * y_ij[i][j] for i in range(self.num_user)) - self.edge_capacity
114 for k in range(self.num_cloud):
115 u_jk[j][k] = y_jk[j][k] * ujk_residual[j]
116 # build objective
117 obj = self._build_objective_components(u_jk, x_edge, y_ij, y_ik)
118 # build equality constraint
119 constraint1, constraint2, constraint3 = self._build_eq_constraint(x_edge, y_ij, y_ik, y_jk)
120 # build inequality constraint
121 ineq_qubo1, ineq_qubo2 = self._build_ineq_constraint(max_ujk, ujk_residual, y_ij, y_jk)
122
123 # building the final model
124 self.qubo_model = kw.qubo.QuboModel()
125 self.qubo_model.set_objective(obj)
126 self.qubo_model.add_constraint(constraint1 == 0, name='c1', penalty=eq_penalties[0])
127 self.qubo_model.add_constraint(constraint2 == 0, name='c2', penalty=eq_penalties[1])
128 self.qubo_model.add_constraint(constraint3 == 0, name='c3', penalty=eq_penalties[2])
129 self.qubo_model.add_constraint(ineq_qubo1 == 0, name='c4', penalty=ineq_penalties[0])
130 self.qubo_model.add_constraint(ineq_qubo2 == 0, name='c5', penalty=ineq_penalties[1])
131
132 def _build_ineq_constraint(self, max_ujk, ujk_residual, y_ij, y_jk):
133 # inequality constraint 1: after subtracting the edge's maximum capacity from demand,
134 # the yjk constraint should hold
135 ineq_constraint1 = []
136 ineq_qubo1 = kw.core.BinaryExpression(coefficient={}, offset=0)
137 len_slack1 = math.ceil(math.log2(max(max_ujk) + 1))
138 slack1 = kw.core.ndarray((self.num_edge, self.num_cloud, len_slack1), 'slack1',
139 kw.core.Binary)
140 for j in range(self.num_edge):
141 ineq_constraint1.append([])
142 for k in range(self.num_cloud):
143 if y_jk[j][k] == 0:
144 ineq_constraint1[j].append(0)
145 else:
146 ineq_constraint1[j].append(
147 ujk_residual[j] - (max_ujk[j] - self.edge_capacity) * y_jk[j][k])
148 ineq_qubo1 += (ineq_constraint1[j][k] + sum(
149 slack1[j][k][_] * (2 ** _) for _ in range(len_slack1))) ** 2
150 # inequality constraint 2: the capacity of an edge should be greater than or equal to the demand
151 ineq_qubo2 = kw.core.BinaryExpression(coefficient={}, offset=0)
152 ineq_constraint2 = []
153 len_slack2 = math.ceil(math.log2(max(max_ujk) + 1))
154 slack2 = kw.core.ndarray((self.num_edge, self.num_cloud, len_slack2), 'slack2',
155 kw.core.Binary)
156 for j in range(self.num_edge):
157 ineq_constraint2.append([])
158 for k in range(self.num_cloud):
159 if y_jk[j][k] == 0:
160 ineq_constraint2[j].append(0)
161 else:
162 ineq_constraint2[j].append(y_jk[j][k] * self.edge_capacity - sum(
163 self.demand[self.user_locations[i]] * y_ij[i][j] for i in range(self.num_user)))
164 ineq_qubo2 += (ineq_constraint2[j][k] + sum(
165 slack2[j][k][_] * (2 ** _) for _ in range(len_slack2))) ** 2
166 return ineq_qubo1, ineq_qubo2
167
168 def _build_eq_constraint(self, x_edge, y_ij, y_ik, y_jk):
169 # constraint 1: ensure that each user's service demand is assigned to only one location (either edge or cloud)
170 constraint1 = 0
171 for i in range(self.num_user):
172 constraint1 += (sum(y_ij[i][j] for j in range(self.num_edge)) + sum(
173 y_ik[i][k] for k in range(self.num_cloud)) - 1) ** 2
174 # constraint 2: initialize constraint expression
175 constraint2 = 0
176 for i in range(self.num_user):
177 for j in range(self.num_edge):
178 if self.coverage[(self.user_locations[i], self.edge_locations[j])] == 0:
179 y_ij[i][j] = 0
180 else:
181 constraint2 += y_ij[i][j] * (1 - x_edge[j])
182 # constraint 3: ensure the relationship between yjk and x_edge
183 constraint3 = 0
184 for j in range(self.num_edge):
185 for k in range(self.num_cloud):
186 constraint3 += y_jk[j][k] * (1 - x_edge[j])
187 return constraint1, constraint2, constraint3
188
189 def _build_objective_components(self, u_jk, x_edge, y_ij, y_ik):
190 # objective function
191 c_fix = sum(self.fix_cost_edge[self.edge_locations[j]] * x_edge[j] for j in range(self.num_edge))
192 c_var = self.var_cost_cloud * sum(sum(self.demand[self.user_locations[i]] * y_ik[i][k]
193 for i in range(self.num_user)) for k in range(self.num_cloud))
194 c_var += self.var_cost_edge * sum(
195 sum(self.demand[self.user_locations[i]] * y_ij[i][j] for i in range(self.num_user))
196 for j in range(self.num_edge))
197 c_var += (self.var_cost_cloud - self.var_cost_edge) * sum(
198 sum(u_jk[j][k] for j in range(self.num_edge)) for k
199 in range(self.num_cloud))
200 c_tran = self.trans_cost_user_edge * sum(sum(
201 self.demand[self.user_locations[i]] * self.distances[(self.user_locations[i], self.edge_locations[j])] *
202 y_ij[i][j] for i in range(self.num_user)) for j in range(self.num_edge))
203 c_tran += self.trans_cost_user_cloud * sum(sum(
204 self.demand[self.user_locations[i]] * self.distances[(self.user_locations[i], self.cloud_locations[k])] *
205 y_ik[i][k] for i in range(self.num_user)) for k in range(self.num_cloud))
206 c_tran += self.trans_cost_edge_cloud * sum(sum(
207 self.distances[(self.edge_locations[j], self.cloud_locations[k])] * u_jk[j][k] for j in
208 range(self.num_edge)) for k in range(self.num_cloud))
209 return c_fix + c_tran + c_var
210
211 def solve(
212 self,
213 max_iterations: int = 10,
214 init_temp: float = 1e3,
215 decay: float = 0.99,
216 min_temp: float = 1e-4,
217 iter_per_temp: int = 10
218 ):
219 """
220 Perform simulated annealing.
221 """
222 best = math.inf
223 for num in range(max_iterations):
224 worker = kw.classical.SimulatedAnnealingOptimizer(
225 initial_temperature=init_temp,
226 alpha=decay,
227 cutoff_temperature=min_temp,
228 iterations_per_t=iter_per_temp
229 )
230 solver = kw.solver.SimpleSolver(worker)
231 sol, val = solver.solve_qubo(self.qubo_model)
232 feasible = self.recovery(sol)
233 if feasible and val < best:
234 best = val
235 print(f"Iter {num}: best={val}")
236 print(f"Optimal={best}")
237
238 def recovery(self, sol_dict: dict) -> bool:
239 """
240 Validate solution via kw.qubo.get_val interface.
241 """
242 unsatisfied_count, _ = self.qubo_model.verify_constraint(sol_dict)
243 return not unsatisfied_count
244
245
246if __name__ == "__main__":
247 # create an instance of the solver class
248 solver = CloudEdgeUserSolver()
249
250 # prepare the data
251 solver.prepare_data()
252
253 # prepare the qubo model, set the penalty coefficient lambda
254 solver.prepare_model()
255
256 # use simulated annealing to find the optimal solution
257 solver.solve()
