Overview#
Kaiwu SDK#
The SDK is a software development kit designed for solving QUBO problems based on coherent optical quantum computers. The kit is dedicated to providing developers with a convenient Python environment to build software algorithms suitable for coherent optical quantum computers and call the quantum computer machine directly through the physical interface (currently supports Ising matrices) for calculations.
The SDK currently includes the following core modules: qubo, cim, ising, preprocess, classical, sampler, solver, and common. In a typical application scenario, the user first uses the qubo module to model the problem, and then uses the solver module to efficiently solve the constructed QUBO model. The solver module is not only responsible for managing the coefficients of the QUBO model, but also supports calling a user-specified optimizer to perform a deep solution to the final Ising model matrix.
We specifically define the solution function of the Ising model matrix as the optimizer. Among them, the optimizers based on classical computing, such as SA, tabu and other classical simulation solvers, are integrated in the classical module; while the optimizer directly connected to the real machine is located in the cim module. In addition, other auxiliary modules provide practical functions such as logging, reduced-order processing and reduced-precision processing, providing users with comprehensive support.
Typical usage#
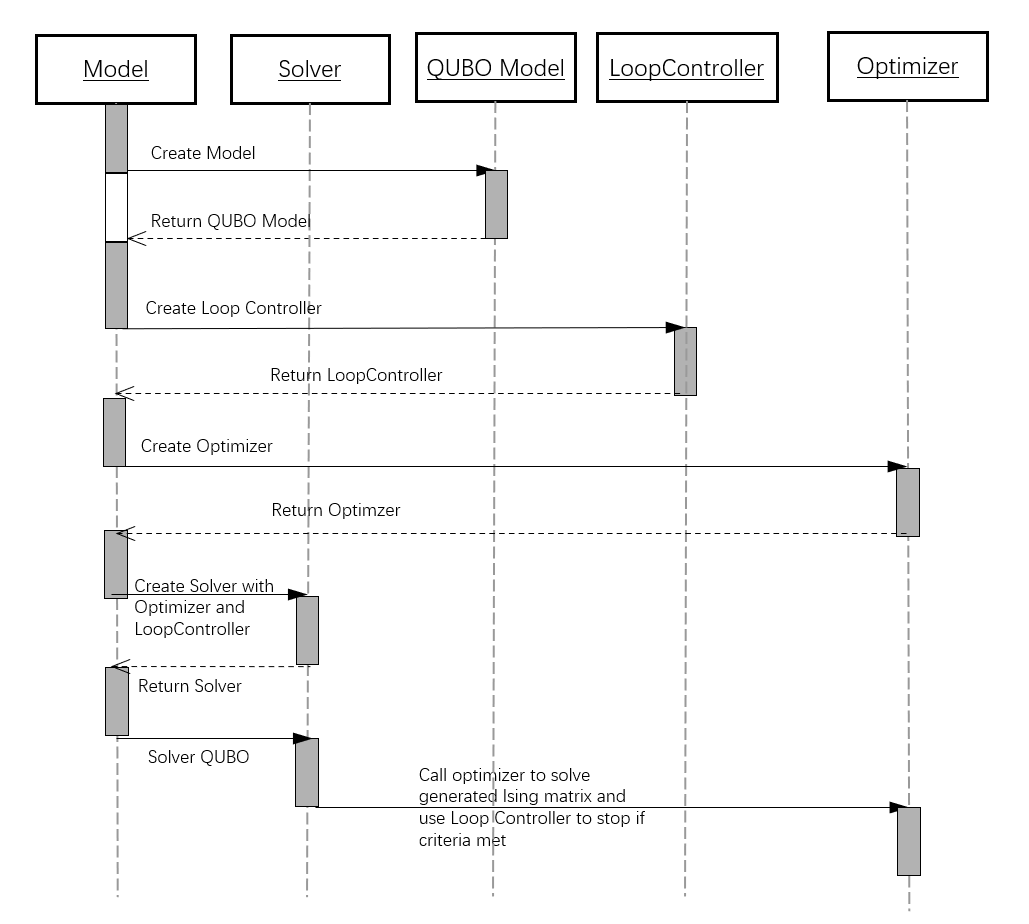
Prerequisites#
CPQC#
CPQC (Coherent Photonic Quantum Computer), is a quantum computer technology that QBoson focuses on developing at present. CPQC is an optical quantum computer based on degenerate optical parametric oscillator (DOPO). In mathematical practice, we can abstract CPQC as a specialized computer for optimizing Ising models.
Ising Model#
Ising Model is a kind of stochastic process model describing the phase transition of substances, with the mathematical form of:
where are spin variables to be solved, taking the values of
.
is the Hamiltonian.
,
,
are quadratic coefficients and linear coefficients respectively.
QUBO#
QUBO (Quadratic unconstrained binary optimization) has the following mathematical form:
where are binary variables to be solved, taking the values of
.
is the objective function.
is the quadratic coefficients, which is given. In the form of linear algebra:
where are variables,
is the QUBO matrix. The objective of QUBO model is to find
to maximize or minimize
, that is:
In Kaiwu SDK, viewing QUBO model details through kw.qubo.details will display offset and coefficients information. Where offset represents the constant term in the QUBO model, which has nothing to do with the variables. coefficients represents the coefficient value of each binary variable in the QUBO model, And the coefficient values of their interaction terms.
Solving Models Using CPQC#
The process of solving QUBO or optimizing Ising model is a process of importing in QUBO or
in Ising to CPQC, and CPQC returns
or
.
Citing Kaiwu SDK#
If the Kaiwu SDK is helpful to your academic research, Bose Quantum thanks you for citing it as follows.
@software{KaiwuSDK,
title = {Kaiwu SDK for development and research on coherent ising machine},
author = {{QBoson Inc.}},
year = {2022},
url = {https://www.qboson.com/}
}
Or
@misc{KaiwuSDK,
title = {Kaiwu SDK for development and research on coherent ising machine},
author = {{QBoson Inc.}},
year = {2022},
url = {https://www.qboson.com/}
}
