Beginner Tutorial - Using the Real Machine - Cloud Platform or SDK#
Use case description#
The whole process from modeling, submitting Qubo matrix to the cloud platform, and obtaining calculation results from the cloud platform is demonstrated through the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP).
Method 1: Upload QUBO matrix calculation through the cloud platform#
Code modeling and generating qubo matrix#
1# pylint: disable=<R0801>
2"""
3TSP problem solved using CIM.
4"""
5import numpy as np
6import pandas as pd
7import kaiwu as kw
8import kaiwu.core._binary_expression
9
10
11def is_edge_used(var_x, var_u, var_v):
12 """
13 Determine whether the edge (u, v) is used in the path.
14
15 Args:
16 var_x (ndarray): Decision variable matrix.
17
18 var_u (int): Start node.
19
20 var_v (int): End node.
21
22 Returns:
23 ndarray: Decision variable corresponding to the edge (u, v).
24 """
25 return kaiwu.core.quicksum([var_x[var_u, j] * var_x[var_v, j + 1] for j in range(-1, n - 1)])
26
27
28if __name__ == '__main__':
29 # Import distance matrix
30 w = np.array([[0, 1, 2],
31 [1, 0, 0],
32 [2, 0, 0]])
33 # Get the number of nodes
34 n = w.shape[0]
35
36 # Create qubo variable matrix
37 x = kaiwu.core.ndarray((n, n), "x", kaiwu.core.Binary)
38
39 # Get sets of edge and non-edge pairs
40 edges = [(u, v) for u in range(n) for v in range(n) if w[u, v] != 0]
41 no_edges = [(u, v) for u in range(n) for v in range(n) if w[u, v] == 0]
42
43 qubo_model = kw.qubo.QuboModel()
44 # TSP path cost
45 qubo_model.set_objective(
46 kaiwu.core.quicksum([w[u, v] * is_edge_used(x, u, v) for u, v in edges]))
47
48 # Node constraint: Each node must belong to exactly one position
49 qubo_model.add_constraint((x.sum(axis=0) - 1) ** 2 == 0, "sequence_cons", penalty=5.0)
50
51 # Position constraint: Each position can have only one node
52 qubo_model.add_constraint((x.sum(axis=1) - 1) ** 2 == 0, "node_cons", penalty=5.0)
53
54 # Edge constraint: Pairs without edges cannot appear in the path
55 qubo_model.add_constraint(kaiwu.core.quicksum([is_edge_used(x, u, v) for u, v in no_edges]) == 0,
56 "connect_cons", penalty=20)
57
58 qubo_mat = qubo_model.get_matrix()
59 pd.DataFrame(qubo_mat).to_csv("tsp.csv", index=False, header=False)
Log in to the cloud platform to upload the matrix#
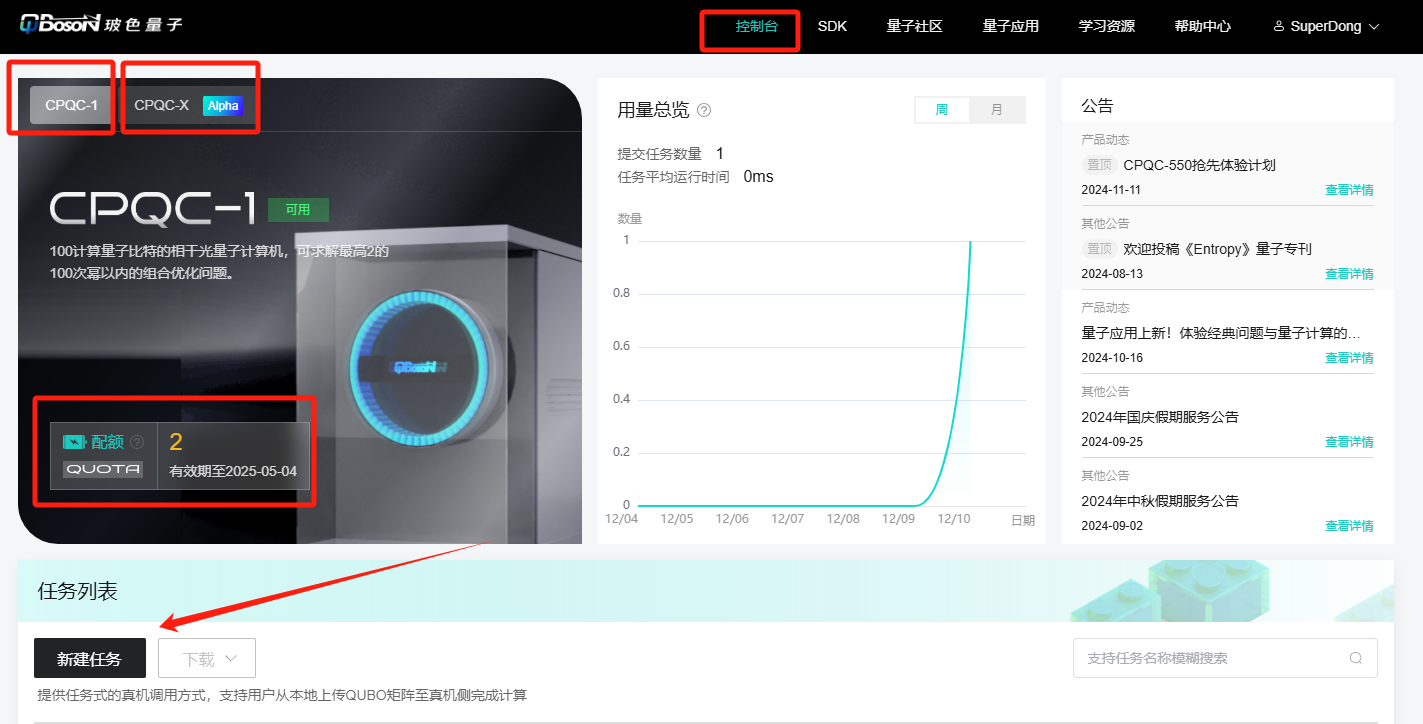
After logging into the Quantum Cloud Computing Platform, enter the console, select the real machine and click Create Task
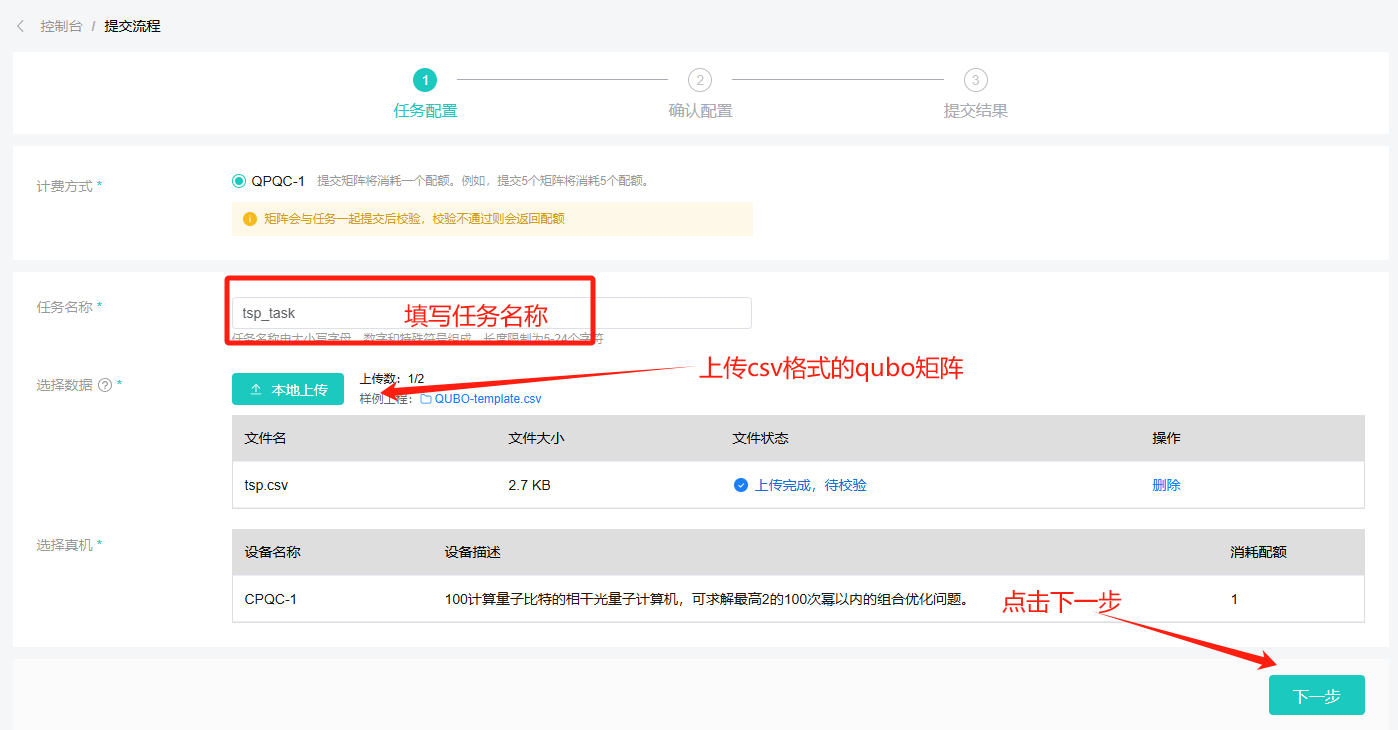
After entering the task configuration page, fill in the task name, upload the matrix, and click Next after confirmation.
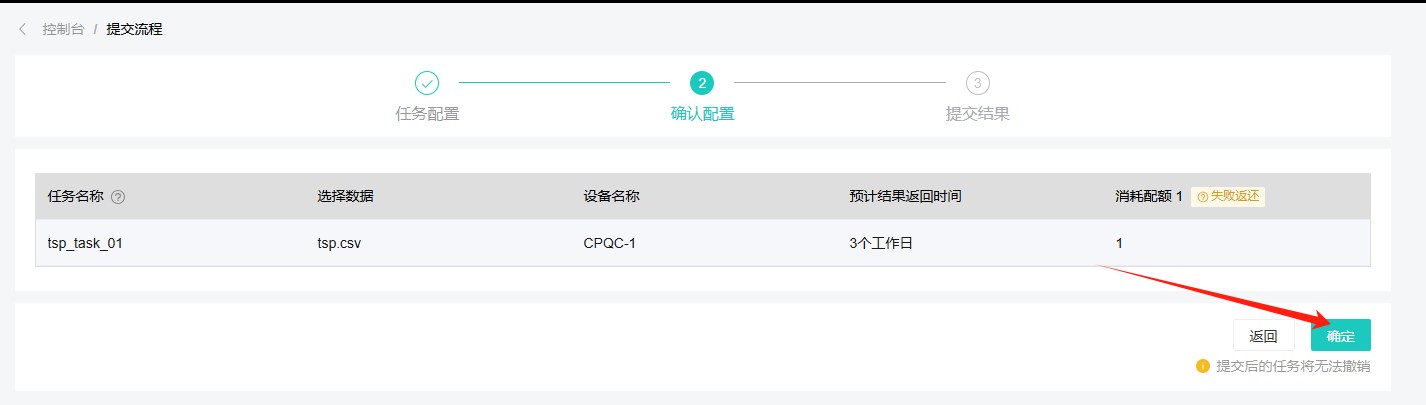
Enter the Confirm Configuration page, confirm the task and real machine information, and click the OK button
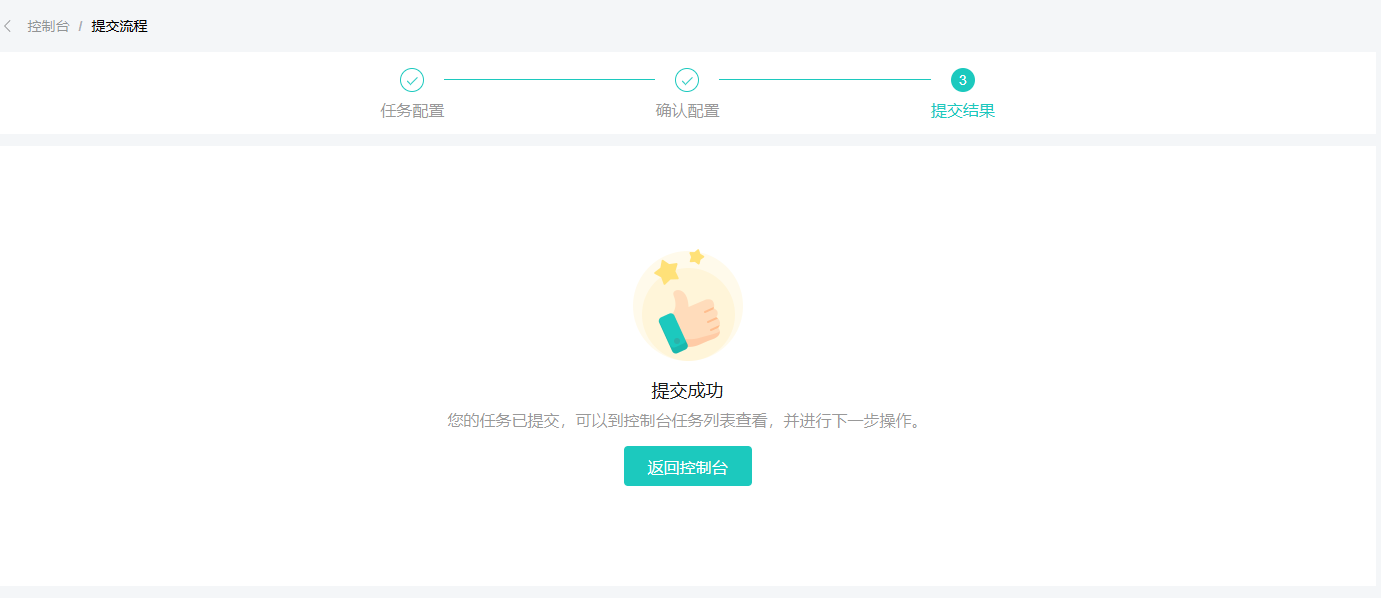
Enter the task submission page, and it will show that the submission is successful.
Return to the console, the task is being verified
After verification is successful, the task enters the queued state
After the task is completed, click Details to enter the result details page
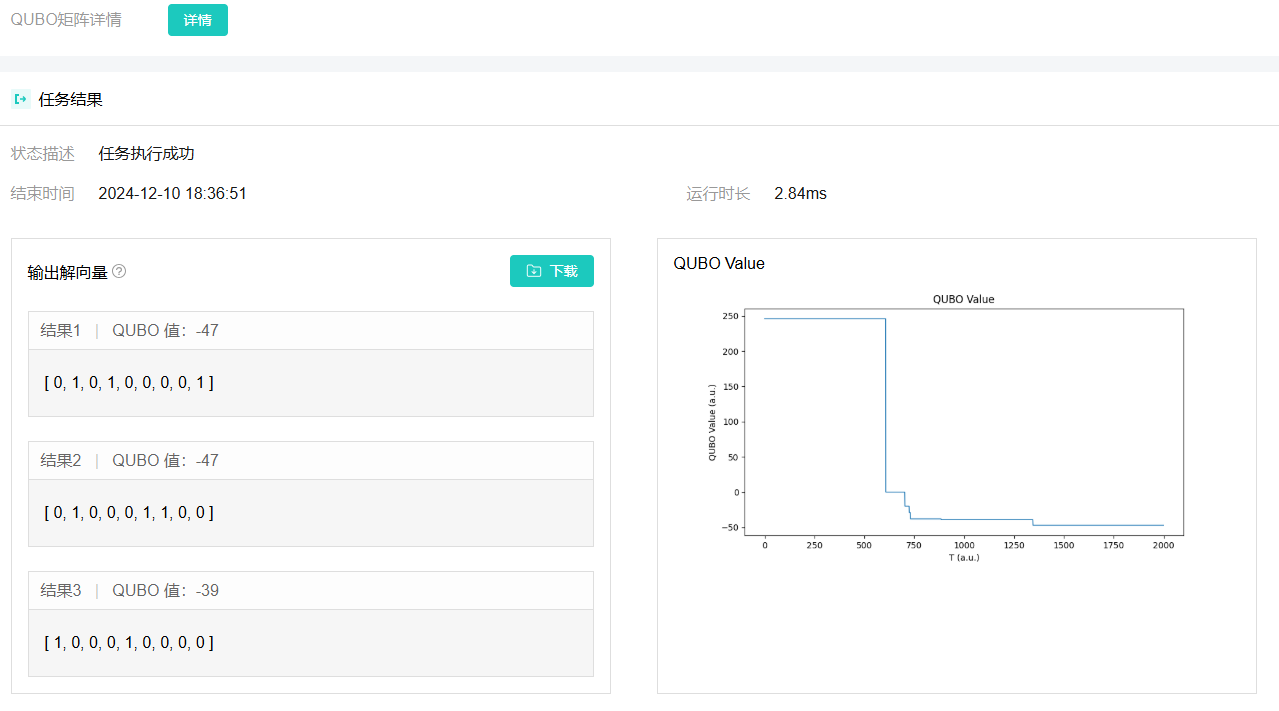
View result details (qubo solution vector, qubo value evolution curve, task execution time, etc.)
Method 2: Directly use the SDK to call the real machine#
The following is an example of using the SDK to directly call the real machine to solve the same TSP problem.Since quantum computers have precision limitations, the PrecisionReducer that comes with the SDK is used for precision adaptation in the example. Want to know more about precision,
See also
1"""
2TSP calling CIM example
3"""
4import kaiwu as kw
5import numpy as np
6from kaiwu.common import CheckpointManager as ckpt
7
8# Define edges using conditional functions
9def is_edge_used(var_x, var_u, var_v):
10 """
11 Determine whether the edge (u, v) is used in the path.
12
13 Args:
14 var_x (ndarray): Decision variable matrix.
15
16 var_u (int): Start node.
17
18 var_v (int): End node.
19
20 Returns:
21 ndarray: Decision variable corresponding to the edge (u, v).
22 """
23 return kw.core.quicksum([var_x[var_u, j] * var_x[var_v, j + 1] for j in range(-1, n - 1)])
24
25
26if __name__ == "__main__":
27 # Set the save path for intermediate files
28 kw.common.CheckpointManager.save_dir = '/tmp'
29 # Define distance matrix
30 w = np.array([[0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
31 [0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
32 [1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
33 [1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
34 [0, 1, 1, 1, 0]])
35
36 n = w.shape[0] # Number of nodes
37
38 # Create a QUBO variable matrix (n x n)
39 x = kw.core.ndarray((n, n), "x", kw.core.Binary)
40
41 # Generate the set of edges and the set of non-edges
42 edges = [(u, v) for u in range(n) for v in range(n) if w[u, v] != 0]
43 no_edges = [(u, v) for u in range(n) for v in range(n) if w[u, v] == 0]
44
45 # Initialize the QUBO model
46 qubo_model = kw.qubo.QuboModel()
47
48 # Set the objective function: minimize path cost
49 path_cost = kw.core.quicksum([w[u, v] * is_edge_used(x, u, v) for u, v in edges])
50 qubo_model.set_objective(path_cost)
51
52 # Add constraints
53 # Node constraints: Each node must occupy one position
54 qubo_model.add_constraint((x.sum(axis=0) - 1) ** 2 == 0, "node_cons", penalty=5.0)
55
56 # Location constraint: Each location must have at least one node.
57 qubo_model.add_constraint((x.sum(axis=1) - 1) ** 2 == 0, "pos_cons", penalty=5.0)
58
59 # Edge constraint: Non-connecting edges must not appear
60 qubo_model.add_constraint(
61 kw.core.quicksum([is_edge_used(x, u, v) for u, v in no_edges])==0,
62 "edge_cons", penalty=5
63 )
64
65 # Configure the solver
66 ckpt.save_dir = './tmp'
67 optimizer = kw.cim.CIMOptimizer(task_name_prefix="tsp")
68 optimizer = kw.cim.PrecisionReducer(optimizer, 8)
69 solver = kw.solver.SimpleSolver(optimizer)
70 sol_dict, qubo_val = solver.solve_qubo(qubo_model)
71
72 if sol_dict is not None:
73 # Verification Results
74 unsatisfied, res_dict = qubo_model.verify_constraint(sol_dict)
75 print(f"Number of unsatisfied constraints: {unsatisfied}")
76 print(f"constraint value: {res_dict}")
77
78 # Calculate path cost
79 path_cost = kw.core.get_val(qubo_model.objective, sol_dict)
80 print(f"Actual path cost: {path_cost}")
81 else:
82 print("Try again later")
